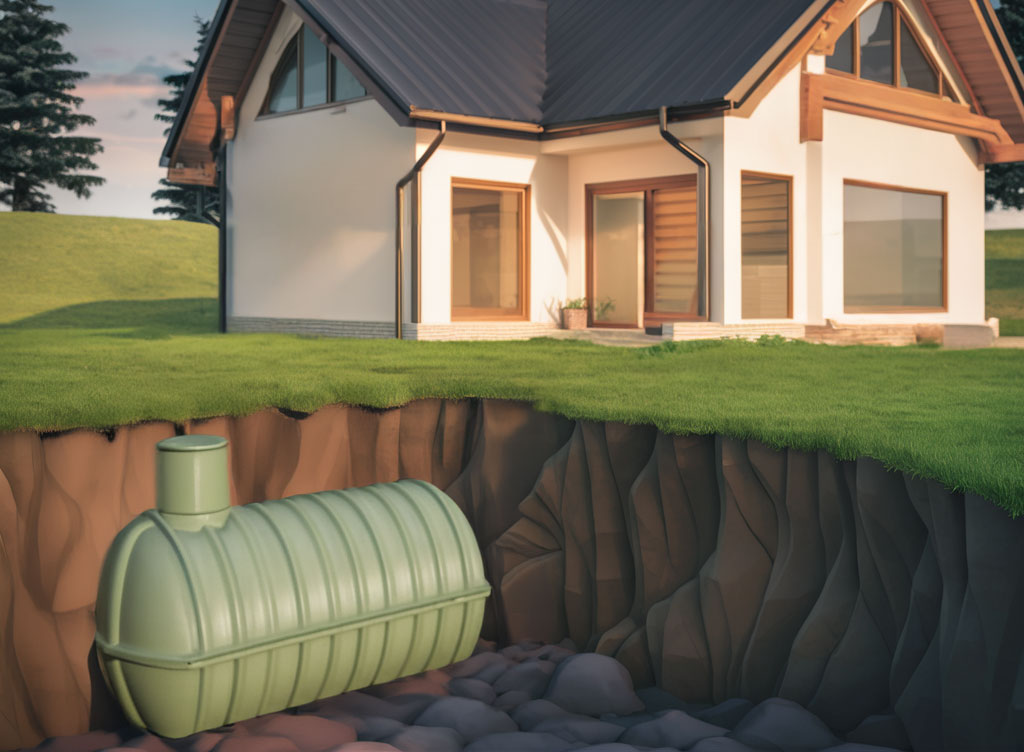
A septic system is a crucial component for homes and cottages in Northern Ontario, particularly in the Muskoka & Haliburton Regions, where municipal sewer systems are not available.
Key Components of a Septic System
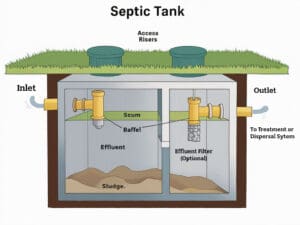
A septic system is an on-site wastewater treatment system that treats and disposes of household sewage. It consists of several key components:
- Septic Tank: The septic tank is a buried, watertight container made of concrete, fiberglass, or polyethylene. It receives all the wastewater from the home, including toilets, sinks, showers, and washing machines. In the tank, solids settle to the bottom, forming a sludge layer, while oils and greases float to the top, creating a scum layer. The partially treated wastewater, known as effluent, flows out of the tank into the next component.
- Distribution Box: The effluent from the septic tank flows into a distribution box, which evenly distributes the liquid among the drain field’s pipes or trenches.
- Drain Field (Leaching Bed): The drain field, also known as a leaching bed, is a network of perforated pipes or trenches surrounded by gravel or crushed stone. The effluent from the distribution box is dispersed into the drain field, where it slowly filters through the soil. The soil acts as a natural filter, removing harmful bacteria, viruses, and nutrients from the wastewater before it reaches the groundwater
Septic System Design and Installation in Muskoka and Haliburton
In Muskoka and Haliburton, septic systems must be designed and installed to meet the unique challenges of the region, such as rocky terrain, high water tables, and cold winters. The Ontario Building Code and local regulations dictate specific requirements for septic system installation:
- Soil Evaluation: A soil evaluation is necessary to determine the soil’s ability to absorb and treat the wastewater effectively. Sandy soils are preferred, as they allow for better drainage and filtration.
- System Size: The size of the septic system, including the septic tank and drain field, is determined by the number of bedrooms in the home, as each bedroom is assumed to have two occupants.
- Setbacks: Septic systems must be installed at a safe distance from wells, surface water bodies, and property lines to prevent contamination.
- Winter Considerations: In Muskoka’s cold climate, septic systems may require additional insulation or heating elements to prevent freezing and ensure proper operation during the winter months.
The Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance, such as pumping the septic tank every 2-5 years (depending on household size), is crucial to ensure the system’s longevity and prevent costly repairs or environmental contamination.

Conclusion
In summary, septic systems play a vital role in wastewater treatment for homes and cottages in the Muskoka region of Northern Ontario. Proper design, installation, and maintenance are essential to ensure these systems function effectively while protecting the region’s pristine lakes and natural environment.